Juniper Publishers| The Experimental Behavioral Model and Software to Identify the Mental Activity of Brain
Journal of Psychology-JuniperPublishers
Abstract
The paper put the general problem; try to identify in the electroencephalogram (EEG) manifestations of mental activity of the brain associated with awareness and the subjective perception of the semantic content of the visual image. For this purpose it is necessary to compare the two states, one of which is characterized by the subjective awareness; another, its absence. To solve this problem at this stage developed an experimental model and software for testing temporary visual discrimination of human abilities, understanding the semantic content of the image with the least of his exposure on the screen.
The experimental model and software allow identifying and comparing performance on electroencephalographic two states of brain activity - in which there is a subjective perception of the meaning of the visual image of a person, and when it is not due to the short duration of the presentation of the visual image.
Keywords: Mental activity of the brain; Consciousness; Information technology; Electroencephalogram; EEG wavelet analysis
Introduction
The brain is a unique organization in nature, having the mental activity, which is manifested in the mind: thoughts, feelings, emotions, i.e., in the subjective human perception of himself and the world. The need to study the nature of the mental activity of the brain indicated [1-9]. The activity of the brain there is a duality: on the one hand, there are neurophysiological processes; On the other hand, there is the associated subjective states representative of all facets of life in the attitude [10,11]. Currently using various electrophysiological, neurochemical, and other magnetic resonance methods and devices can be registered neurophysiological processes in the brain. Neurophysiological studies allow isolate afferent sensory streams that can be used for example for visualization of images. In studies AM Ivanitsky [3] (1999) have shown that the subjective sensation occurs approximately 150 milliseconds after the application of a visual stimulus, i.e. much later arrival of sensory impulses in the visual cortex, which takes just 30 ms. It should be borne in mind that the visual perception of an image does not mean a conscious understanding of its semantic content, which requires much more time.
The neurophysiological processes also presents effectors mechanisms run the motor, motor-speech, mimic, autonomic reactions. In fact, all the existing techniques in psychophysiology and neurophysiology not allow itself to capture and study the patterns of mental activity of the brain: the thoughts, emotions, feelings, mechanisms which are beyond the objective scientific study [10,11].
This explains the "dip" between the understanding of mental and neurophysiological phenomena in the brain, which indicates T. Nagel [6] (2010). The disclosure of the nature of mental activity of the brain and eliminate this "failure" is necessary to develop a radically new methodology to decipher in neurophysiological processes manifestations (patterns) of mental activity of the brain.
At the present time was developed advanced mathematical method of wavelet analysis of the electroencephalogram (EEG), which opens up new possibilities for identifying the content of brain processes (AA Koronovskii [12] et al, 2013;.. AE Hramov at al. [13] 2015) and in particular mental activity of the brain. The essence of the study is to compare the electroencephalographic manifestations of human brain activity when two states - one of which is characterized by the subjective perception of the visual image, the other, the lack of it. To solve this problem in the first phase is necessary to develop an experimental model and software for testing temporary visual discriminatory human ability to realize the semantic content of the image with the least of his exposure on the screen.
Results
Developed information and software can detect and compare the two figures on the state of electroencephalographic brain activity - in which there is a subjective perception of the visual image of a person, and when it is not due to the short duration of the presentation of the visual image. The experimental setup based PC has two monitors are used at the same time during the test. The first monitor is designed for the experimenter, who produces the setting in the main window "Window experimenter" program parameters: the number of consecutively exposed images images, the exposure time of the first image, the reduction of the exposure time subsequent, image clarity.
The second monitor, which displays visual images in full screen mode for the subject. On this subject the monitor sees "window of exposure". This window appears in series with the series of images decrease the exposure time. The subject should look carefully at the screen and be aware of the on-screen image. At a certain minimum exposure time on the screen flashed the subject sees the image, but do not have time to realize its semantic content. After the test, each subject according to which image he comprehended, and what the image could not realize due to the short duration of exposure. During the tests carried out registration and EEG recording, further comparative EEG wavelet analysis in two test conditions: in the presence of subjective awareness and image in the absence of understanding the semantic content of the image.
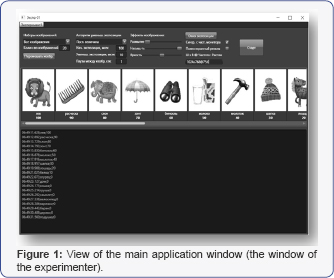
We have created a computer program based on (M. MacDonald [14] 2012; Justin Stenning [15] 2014) easy to use and has an interface in Russian. The program is intended for use on a computer running Windows 8, with two displays - one is management of the program window, on the other - image exposure window for the test (Figures 1 & 2).

The program has experimental magazine, which reflects the start time exposure image, the name of the pattern and duration of the exposure image in milliseconds. The magazine is displayed in the main window to the experimenter, and stored in a file located in the Results directory. The file is automatically assigned a name containing the date and time of the experiment. The program contains a database of images, including 68 drawings, with an easily identifiable visual images: animals, plants, household items, furniture, transport. Images have sufficient resolution (300 dpi), and are presented in color. Each figure is depicted vividly and clearly.
The program allows you to randomly generate a set of images successively appear on the screen each time. This makes it possible to avoid the subject of addiction and its stereotyped answers. Updating the sequence of images by clicking on the button "Shuffle". The experimenter can set the number of images; the program will be displayed on the screen for a test in a special window "Number of images". The program also has the ability to change the sharpness, color saturation, and brightness of the images. To do this, there are regulators, "Blur", "Saturation", and "Brightness". By changing these parameters, you can make the image more or less recognizable.
The program allows you to change the time between the presentations of images, t. E. The length of the pause between images. To do this in the "Pause between images" field, you can set the number of seconds between the two pictures will take a break. At this time the test will see a white screen. Time exposure image is always a multiple of the time you upgrade a computer display screen. For example, when the monitor is 60 Hz, the minimum picture display time will be equal to 1/60 a 16.7 ms.On such a screen will be displayed with pictures of duration 17, 34, ... 51 ms, depending on the exposure value in the program.
In order to achieve the minimum time of exposure, it is necessary to use a larger screen refresh rate. For example, for a screen with a maximum frequency of 75 Hz, the exposure time will be a multiple ≈13.3ms for 85 Hz ≈ 11.8, etc. To set the minimum exposure time, it is necessary to determine the optimal display mode (display resolution for the maximum refresh rate) in the settings of the Windows operating system, and specify it in the "W x H @ Frequency: extensible", eg "1024x768 @ 75: 0" After that, switch the exposure window in the "Full Screen"
The experimenter can change the time of presentation of the image. The program can work in two algorithms reduce exposure:
- Reduction of the subsequent image exposure time 2-fold;
- Reduction in exposure time to a constant value. In the "Initial exposure" can be set for how many milliseconds will be displayed on the first image from the set of the screen. The "Reduction of exposure" sets the time, in milliseconds, at which decreases the next image exposure.
When you run the program initially opens the window for the experimenter. In this window you can see all the buttons, as well as the set of images described above with the names, which will see the subject. The numbers under the drawings shows the time in milliseconds, during which the program will expose the image. If this time is not a multiple of the minimum refresh time, the image will last a little longer - until the next screen refresh. "The window of exposure" button activates the window to display the subject image. This window opens automatically when you press the "Start" button, which starts the experiment. After clicking on "Start", she immediately renamed the "Stop" button, clicking on it; you can at any time to stop the experiment.
To control two monitors should select the graphic characteristics of the screen "Extended Desktop". After this, "Window of the experimenter" brings on the main monitor and the "window of exposure" - on the secondary monitor. Thus, in the course of the study and, depending on the tasks experimenter can change various parameters in the program. Used in an experimental model of technique changes the volume, clarity of information signs and time exposure image allows you to individually identify the two different states of the subjects, when one of them holds a visual interpretation of the image, while the other, there is no awareness of its semantic content.
Conclusion
Result is:
- The program for the PC that allows you to identify the individual person's ability to realize the time semantic content of the visual image.
- An experimental setup for the PC-based test and identify the various states of human brain activity - one of which is characterized by the subjective perception of the visual image, the other, the lack of it.
Information and software can serve as experimental psychological tests to identify the individual characteristics of the time of the subjective awareness of the visual image. Experimental set-up on the basis of PC and software can be used to identify the temporary threshold of subjective awareness of the visual image of healthy and neuropsychiatric patients.
To read more articles in Journal of Psychology and Behavior Please Click on https://juniperpublishers.com/pbsij/index.php
For More Open Access Journals in Juniper Publishers
Click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/journals.php

Comments
Post a Comment